- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Why should make career in advance computer hardware ?
Defination:
Hardware represents the physical and tangible components of a computer, i.e. the components that can be seen and touched.
Examples of Hardware are the following −
- Input devices − keyboard, mouse, etc.
- Output devices − printer, monitor, etc.
- Secondary storage devices − Hard disk, CD, DVD, etc.
- Internal components − CPU, motherboard, RAM, etc.

Relationship between Hardware and Software
- Hardware and software are mutually dependent on each other. Both of them must work together to make a computer produce a useful output.
- Software cannot be utilized without supporting hardware.
- Hardware without a set of programs to operate upon cannot be utilized and is useless.
- To get a particular job done on the computer, relevant software should be loaded into the hardware.
- Hardware is a one-time expense.
- Software development is very expensive and is a continuing expense.
- Different software applications can be loaded on a hardware to run different jobs.
- A software acts as an interface between the user and the hardware.
- If the hardware is the ‘heart’ of a computer system, then the software is its ‘soul’. Both are complementary to each other.
Software is a set of programs, which is designed to perform a well-defined function. A program is a sequence of instructions written to solve a particular problem.
There are two types of software −
- System Software
- Application Software
System Software
The system software is a collection of programs designed to operate, control, and extend the processing capabilities of the computer itself. System software is generally prepared by the computer manufacturers. These software products comprise of programs written in low-level languages, which interact with the hardware at a very basic level. System software serves as the interface between the hardware and the end users.
Some examples of system software are Operating System, Compilers, Interpreter, Assemblers, etc.

Here is a list of some of the most prominent features of a system software −
- Close to the system
- Fast in speed
- Difficult to design
- Difficult to understand
- Less interactive
- Smaller in size
- Difficult to manipulate
- Generally written in low-level language
Application Software
Application software products are designed to satisfy a particular need of a particular environment. All software applications prepared in the computer lab can come under the category of Application software.
Application software may consist of a single program, such as Microsoft’s notepad for writing and editing a simple text. It may also consist of a collection of programs, often called a software package, which work together to accomplish a task, such as a spreadsheet package.
Examples of Application software are the following −
- Payroll Software
- Student Record Software
- Inventory Management Software
- Income Tax Software
- Railways Reservation Software
- Microsoft Office Suite Software
- Microsoft Word
- Microsoft Excel
- Microsoft PowerPoint

Features of application software are as follows −
- Close to the user
- Easy to design
- More interactive
- Slow in speed
- Generally written in high-level language
- Easy to understand
- Easy to manipulate and use
- Bigger in size and requires large storage space
Hardware Technology:
- Microprocessor and its Troubleshooting:
Microprocessor is the brain of computer, which does all the work. It is a computer processor that incorporates all the functions of CPU (Central Processing Unit) on a single IC (Integrated Circuit) or at the most a few ICs. Microprocessors were first introduced in early 1970s. 4004 was the first general purpose microprocessor used by Intel in building personal computers. Arrival of low cost general purpose microprocessors has been instrumental in development of modern society the way it has.
We will study the characteristics and components of a microprocessor in detail.
Microprocessors Characteristics
Microprocessors are multipurpose devices that can be designed for generic or specialized functions. The microprocessors of laptops and smartphones are general purpose whereas ones designed for graphical processing or machine vision are specialized ones. There are some characteristics that are common to all microprocessors.
These are the most important defining characteristics of a microprocessor −
- Clock speed
- Instruction set
- Word size
Clock Speed
Every microprocessor has an internal clock that regulates the speed at which it executes instructions and also synchronizes it with other components. The speed at which the microprocessor executes instructions is called clock speed. Clock speeds are measured in MHz or GHz where 1 MHz means 1 million cycles per second whereas 1 GHz equals to 1 billion cycles per second. Here cycle refers to single electric signal cycle.
Currently microprocessors have clock speed in the range of 3 GHz, which is maximum that current technology can attain. Speeds more than this generate enough heat to damage the chip itself. To overcome this, manufacturers are using multiple processors working in parallel on a chip.
Word Size
Number of bits that can be processed by a processor in a single instruction is called its word size. Word size determines the amount of RAM that can be accessed at one go and total number of pins on the microprocessor. Total number of input and output pins in turn determines the architecture of the microprocessor.
First commercial microprocessor Intel 4004 was a 4-bit processor. It had 4 input pins and 4 output pins. Number of output pins is always equal to the number of input pins. Currently most microprocessors use 32-bit or 64-bit architecture.
Instruction Set
A command given to a digital machine to perform an operation on a piece of data is called an instruction. Basic set of machine level instructions that a microprocessor is designed to execute is called its instruction set. These instructions do carry out these types of operations −
- Data transfer
- Arithmetic operations
- Logical operations
- Control flow
- Input/output and machine control
Microprocessor Components
Compared to the first microprocessors, today’s processors are very small but still they have these basic parts right from the first model −
- CPU
- Bus
- Memory
CPU:
CPU is fabricated as a very large scale integrated circuit and has these parts −
- Instruction register − It holds the instruction to be executed.
- Decoder − It decodes (converts to machine level language) the instruction and sends to the ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit).
- ALU − It has necessary circuits to perform arithmetic, logical, memory, register and program sequencing operations.
- Register − It holds intermediate results obtained during program processing. Registers are used for holding such results rather than RAM because accessing registers is almost 10 times faster than accessing RAM.
Bus:
Connection lines used to connect the internal parts of the microprocessor chip is called bus. There are three types of buses in a microprocessor −
- Data Bus − Lines that carry data to and from memory are called data bus. It is a bidirectional bus with width equal to word length of the microprocessor.
- Address Bus − It is a unidirectional responsible for carrying address of a memory location or I/O port from CPU to memory or I/O port.
- Control Bus − Lines that carry control signals like clock signals, interrupt signal or ready signal are called control bus. They are bidirectional. Signal that denotes that a device is ready for processing is called ready signal. Signal that indicates to a device to interrupt its process is called an interrupt signal.
Memory:
Microprocessor has two types of memory
- RAM − Random Access Memory is volatile memory that gets erased when power is switched off. All data and instructions are stored in RAM.
- ROM − Read Only Memory is non-volatile memory whose data remains intact even after power is switched off. Microprocessor can read from it any time it wants but cannot write to it. It is preprogrammed with most essential data like booting sequence by the manufacturer.
TROUBLESHOOTING:
- Improper drivers or incompatible hardware.
- Update drivers and check for compatibility issues.
- Check monitor and power to monitor.
- Replace with known-good spare for testing.
- If during the POST the processor is not identified correctly, your motherboard settings might be incorrect or your BIOS might need to be updated.
- Memory and its Troubleshooting:
A memory is just like a human brain. It is used to store data and instructions. Computer memory is the storage space in the computer, where data is to be processed and instructions required for processing are stored. The memory is divided into large number of small parts called cells. Each location or cell has a unique address, which varies from zero to memory size minus one. For example, if the computer has 64k words, then this memory unit has 64 * 1024 = 65536 memory locations. The address of these locations varies from 0 to 65535.
Memory is primarily of three types −
- Cache Memory
- Primary Memory/Main Memory
- Secondary Memory
1. Cache Memory
Cache memory is a very high speed semiconductor memory which can speed up the CPU. It acts as a buffer between the CPU and the main memory. It is used to hold those parts of data and program which are most frequently used by the CPU. The parts of data and programs are transferred from the disk to cache memory by the operating system, from where the CPU can access them.
Advantages
The advantages of cache memory are as follows −
- Cache memory is faster than main memory.
- It consumes less access time as compared to main memory.
- It stores the program that can be executed within a short period of time.
- It stores data for temporary use.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of cache memory are as follows −
- Cache memory has limited capacity.
- It is very expensive.
2. Primary Memory (Main Memory)
Primary memory holds only those data and instructions on which the computer is currently working. It has a limited capacity and data is lost when power is switched off. It is generally made up of semiconductor device. These memories are not as fast as registers. The data and instruction required to be processed resides in the main memory. It is divided into two subcategories RAM and ROM.
Characteristics of Main Memory
- These are semiconductor memories.
- It is known as the main memory.
- Usually volatile memory.
- Data is lost in case power is switched off.
- It is the working memory of the computer.
- Faster than secondary memories.
- A computer cannot run without the primary memory.
3. Secondary Memory
This type of memory is also known as external memory or non-volatile. It is slower than the main memory. These are used for storing data/information permanently. CPU directly does not access these memories, instead they are accessed via input-output routines. The contents of secondary memories are first transferred to the main memory, and then the CPU can access it. For example, disk, CD-ROM, DVD, etc.

Characteristics of Secondary Memory
- These are magnetic and optical memories.
- It is known as the backup memory.
- It is a non-volatile memory.
- Data is permanently stored even if power is switched off.
- It is used for storage of data in a computer.
- Computer may run without the secondary memory.
- Slower than primary memories.
RAM (RANDOM ACCESS MEMMORY):
RAM (Random Access Memory) is the internal memory of the CPU for storing data, program, and program result. It is a read/write memory which stores data until the machine is working. As soon as the machine is switched off, data is erased.
Access time in RAM is independent of the address, that is, each storage location inside the memory is as easy to reach as other locations and takes the same amount of time. Data in the RAM can be accessed randomly but it is very expensive.
RAM is volatile, i.e. data stored in it is lost when we switch off the computer or if there is a power failure. Hence, a backup Uninterruptible Power System (UPS) is often used with computers. RAM is small, both in terms of its physical size and in the amount of data it can hold.
RAM is of two types −
- Static RAM (SRAM)
- Dynamic RAM (DRAM)
Static RAM (SRAM)
The word static indicates that the memory retains its contents as long as power is being supplied. However, data is lost when the power gets down due to volatile nature. SRAM chips use a matrix of 6-transistors and no capacitors. Transistors do not require power to prevent leakage, so SRAM need not be refreshed on a regular basis.
There is extra space in the matrix, hence SRAM uses more chips than DRAM for the same amount of storage space, making the manufacturing costs higher. SRAM is thus used as cache memory and has very fast access.
Characteristic of Static RAM
- Long life
- No need to refresh
- Faster
- Used as cache memory
- Large size
- Expensive
- High power consumption
Dynamic RAM (DRAM)
DRAM, unlike SRAM, must be continually refreshed in order to maintain the data. This is done by placing the memory on a refresh circuit that rewrites the data several hundred times per second. DRAM is used for most system memory as it is cheap and small. All DRAMs are made up of memory cells, which are composed of one capacitor and one transistor.
Characteristics of Dynamic RAM
- Short data lifetime
- Needs to be refreshed continuously
- Slower as compared to SRAM
- Used as RAM
- Smaller in size
- Less expensive
- Less power consumption
ROM (READ ONLY MEMORY):
ROM stands for Read Only Memory. The memory from which we can only read but cannot write on it. This type of memory is non-volatile. The information is stored permanently in such memories during manufacture. A ROM stores such instructions that are required to start a computer. This operation is referred to as bootstrap. ROM chips are not only used in the computer but also in other electronic items like washing machine and microwave oven.
Advantages of ROM
The advantages of ROM are as follows −
- Non-volatile in nature
- Cannot be accidentally changed
- Cheaper than RAMs
- Easy to test
- More reliable than RAMs
- Static and do not require refreshing
- Contents are always known and can be verified
TROUBLESHOTTING:
- Make sure you have the right memory part for your computer. At the manufacturer’s Web site you can look up the part number.
- Confirm that you configured the memory correctly.
- Re-install the module.
- Swap modules.
- Clean the socket and pins on the memory module.
- Update the BIOS.
- Motherboard and its troubleshooting :
The motherboard serves as a single platform to connect all of the parts of a computer together. It connects the CPU, memory, hard drives, optical drives, video card, sound card, and other ports and expansion cards directly or via cables. It can be considered as the backbone of a computer.

Features of Motherboard
A motherboard comes with following features −
- Motherboard varies greatly in supporting various types of components.
- Motherboard supports a single type of CPU and few types of memories.
- Video cards, hard disks, sound cards have to be compatible with the motherboard to function properly.
- Motherboards, cases, and power supplies must be compatible to work properly together.
Popular Manufacturers
Following are the popular manufacturers of the motherboard.
- Intel
- ASUS
- AOpen
- ABIT
- Biostar
- Gigabyte
- MSI
Description of Motherboard
The motherboard is mounted inside the case and is securely attached via small screws through pre-drilled holes. Motherboard contains ports to connect all of the internal components. It provides a single socket for CPU, whereas for memory, normally one or more slots are available. Motherboards provide ports to attach the floppy drive, hard drive, and optical drives via ribbon cables. Motherboard carries fans and a special port designed for power supply.
There is a peripheral card slot in front of the motherboard using which video cards, sound cards, and other expansion cards can be connected to the motherboard.
On the left side, motherboards carry a number of ports to connect the monitor, printer, mouse, keyboard, speaker, and network cables. Motherboards also provide USB ports, which allow compatible devices to be connected in plug-in/plug-out fashion. For example, pen drive, digital cameras, etc.
TROUBLESHOOTING:
Is the motherboard receiving power? Check the power supply to see if the fan is turning. If the CPU or motherboard has a fan, see if it is turning. Check voltages going from the power supply to the motherboard. Check the BIOS/UEFI settings for accuracy. Check for overheating. Power down the computer and allow the computer to cool. Power on the computer with the cover off.
- Check the motherboard for distended capacitors. These are small components that might appear to be bulging. If sighted, replace the motherboard as soon as possible.
- Reseat the CPU, adapters, and memory chips.
- Remove unnecessary adapters and devices and boot the computer.
- Plug the computer into a different power outlet and circuit, if possible.
- Check to determine whether the motherboard is shorting out on the frame.
- Check the CMOS battery.
- With a motherboard that has diagnostic LEDs, check the output for any error code. Refer to the motherboard documentation or online documentation for the problem and possible solution.
- Power supply and its troubleshooting:
Supplies power throughout the computer. Power supplies converts potentially lethal 110-115 or 220-230 volt alternating current (AC) into a steady low-voltage direct current (DC) usable by the computer. A power supply is rated by the number of watts it generates.
A typical PC needs about 250W . AC – alternating current comes from the outlet.DC – direct current goes to the PC. Electrons – A flow of negatively charged particles called electrons
Two types of Power supply:
AT and ATX power supply. ATX has a special power soft switch that can enable the PC to go into suspend or sleep mode.
AT uses the P8 and P9 as the main connectors where it connects to the AT socket of the motherboard. When installing P8/P9 black wires which represent ground must face each other and clips face out. ATX uses the P1 power connector and goes directly into the ATX socket P1 can either be 20 or 24pins for the newer computers.
Note some P1 also have a P4 connector(12v), P6, P8 connectors as add- ones .
Molex Connector : Molex connector can connect to the following devices: All forms of CD/DVD devices, Internal hard drives, tape drives, superdrives, zip drives, fan, video adapters and internal SCSI devices.
Mini-Connector: Mini connector can connect to a floppy drive.
Power Supply Troubleshooting:
It is Plugged In, Check Connection, It is Turn on, Check AC Outlet, Check On and Off Switch on back of PC, Check Voltage, Check Motherboard power sockets if its good or not. To Test Power Supply use a Multimeter or a Power Tester. (if power supply is bad then replace it) Also Check for Dust, Cooling Fan, and if PC keeps rebooting on its own constantly its overheating. Check for weird and unusual noises Power Supply should have a quiet humming noise if it’s good.
- Hard disk drive and its troubleshooting:
Hard disk drive is made up of a series of circular disks called platters arranged one over the other almost ½ inches apart around a spindle. Disks are made of non-magnetic material like aluminum alloy and coated with 10-20 nm of magnetic material.
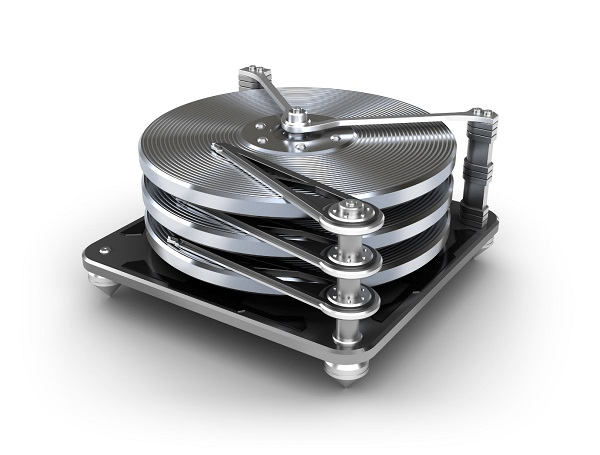
Standard diameter of these disks is 14 inches and they rotate with speeds varying from 4200 rpm (rotations per minute) for personal computers to 15000 rpm for servers. Data is stored by magnetizing or demagnetizing the magnetic coating. A magnetic reader arm is used to read data from and write data to the disks. A typical modern HDD has capacity in terabytes (TB).
TROUBLESHOOTING:
- Hard drive recovery is necessary for failed drives in computers without scheduled backups.
- Pay Attention to the Sounds the Drive is Making.
- Turn Off Your Computer.
- Check Your Connections.
- Look For Your Drive in Your BIOS.
- Put the Drive in an External Enclosure.
- Don’t Ever Open Your Drive.
- Optical Drive:
CD Drive
CD stands for Compact Disk. CDs are circular disks that use optical rays, usually lasers, to read and write data. They are very cheap as you can get 700 MB of storage space for less than a dollar. CDs are inserted in CD drives built into CPU cabinet. They are portable as you can eject the drive, remove the CD and carry it with you. There are three types of CDs −
- CD-ROM (Compact Disk – Read Only Memory) − The data on these CDs are recorded by the manufacturer. Proprietary Software, audio or video are released on CD-ROMs.
- CD-R (Compact Disk – Recordable) − Data can be written by the user once on the CD-R. It cannot be deleted or modified later.
- CD-RW (Compact Disk – Rewritable) − Data can be written and deleted on these optical disks again and again.
DVD Drive
DVD stands for Digital Video Display. DVD are optical devices that can store 15 times the data held by CDs. They are usually used to store rich multimedia files that need high storage capacity. DVDs also come in three varieties – read only, recordable and rewritable.

- I/O ports and Devices:
A connection point that acts as interface between the computer and external devices like mouse, printer, modem, etc. is called port. Ports are of two types −
- Internal port − It connects the motherboard to internal devices like hard disk drive, CD drive, internal modem, etc.
- External port − It connects the motherboard to external devices like modem, mouse, printer, flash drives, etc.
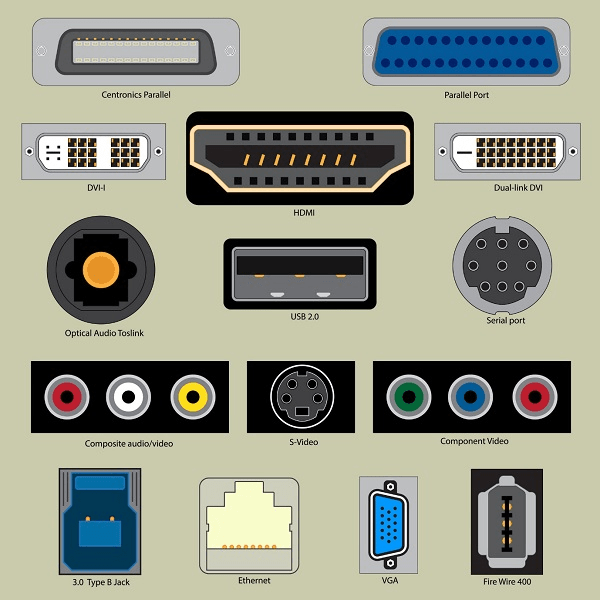
Let us look at some of the most commonly used ports.
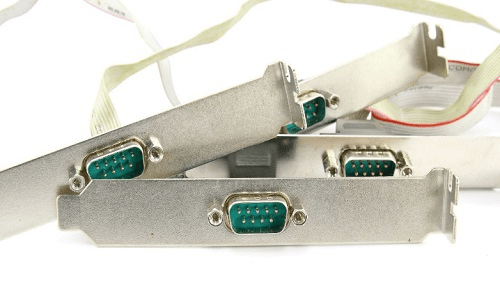
Serial Port
Serial ports transmit data sequentially one bit at a time. So they need only one wire to transmit 8 bits. However it also makes them slower. Serial ports are usually 9-pin or 25-pin male connectors. They are also known as COM (communication) ports or RS323C ports.
Parallel Port
Parallel ports can send or receive 8 bits or 1 byte at a time. Parallel ports come in form of 25-pin female pins and are used to connect printer, scanner, external hard disk drive, etc.
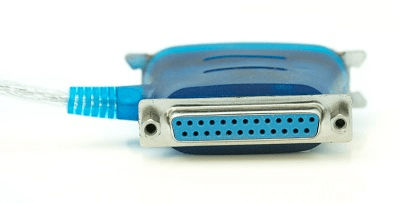
USB Port
USB stands for Universal Serial Bus. It is the industry standard for short distance digital data connection. USB port is a standardized port to connect a variety of devices like printer, camera, keyboard, speaker, etc.

PS-2 Port
PS/2 stands for Personal System/2. It is a female 6-pin port standard that connects to the male mini-DIN cable. PS/2 was introduced by IBM to connect mouse and keyboard to personal computers. This port is now mostly obsolete, though some systems compatible with IBM may have this port.
Infrared Port
Infrared port is a port that enables wireless exchange of data within a radius of 10m. Two devices that have infrared ports are placed facing each other so that beams of infrared lights can be used to share data.
Bluetooth Port
Bluetooth is a telecommunication specification that facilitates wireless connection between phones, computers and other digital devices over short range wireless connection. Bluetooth port enables synchronization between Bluetooth-enabled devices. There are two types of Bluetooth ports −
- Incoming − It is used to receive connection from Bluetooth devices.
- Outgoing − It is used to request connection to other Bluetooth devices.
FireWire Port
FireWire is Apple Computer’s interface standard for enabling high speed communication using serial bus. It is also called IEEE 1394 and used mostly for audio and video devices like digital camcorders.
- Keyboard and Mouse:
KEYBOARD:
A device that lets you type information into the computer.

A keyboard is the most basic input device for computers. It is basically a rectangular piece with over a 100 buttons representing characters, numbers and computer functions. The keyboard layout is popularly called QWERTY, simply because they are the first six characters you will find in the first row. Developed by Christopher Latham Sholes, this layout dates back over a 100 years, and was actually designed to slow a typist down. This is because the hammers of mechanical type writers that typed each letter used to jam when pressed in quick succession. So, Sholes moved the most commonly used letters away from each other. In the 1930s, August Dvorak redesigned it to make it easier to type, but the Dvorak keyboard never really caught on. Keyboard technology has advanced to make the keyboard more ergonomic. Wireless keyboards have also been invented. Prices have come down and buttons to activate and control software such as Web browsers and media players have been added. Keyboard shortcuts are used extensively in today’s PCs. Even handheld devices that lack a real keyboard often provide text input through an on screen keyboar
Available in PS/2 or USB. Keyboard Manufacturer: Belkin, Logitech and Microsoft mouse.
A small hand device used to interact with GUI such as Windows OS and X Windows by Linux. Consider USB models for the easiest hookup and versatility.
MOUSE: Most interactions with a computer involve using a keyboard and a mouse. The keyboard allows the user to type letters and numbers and the mouse allows the user to position the cursor, draw and execute program functions by clicking mouse buttons. Alphanumeric area with letters, numbers, and some control keys.
- Monitor:
Monitors, commonly called as Visual Display Unit (VDU), are the main output device of a computer. It forms images from tiny dots, called pixels that are arranged in a rectangular form. The sharpness of the image depends upon the number of pixels.
There are two kinds of viewing screen used for monitors.
- Cathode-Ray Tube (CRT)
- Flat-Panel Display
Cathode-Ray Tube (CRT) Monitor
The CRT display is made up of small picture elements called pixels. The smaller the pixels, the better the image clarity or resolution. It takes more than one illuminated pixel to form a whole character, such as the letter ‘e’ in the word help.

A finite number of characters can be displayed on a screen at once. The screen can be divided into a series of character boxes – fixed location on the screen where a standard character can be placed. Most screens are capable of displaying 80 characters of data horizontally and 25 lines vertically.
There are some disadvantages of CRT −
- Large in Size
- High power consumption
Flat-Panel Display Monitor
The flat-panel display refers to a class of video devices that have reduced volume, weight and power requirement in comparison to the CRT. You can hang them on walls or wear them on your wrists. Current uses of flat-panel displays include calculators, video games, monitors, laptop computer, and graphics display.

The flat-panel display is divided into two categories −
- Emissive Displays − Emissive displays are devices that convert electrical energy into light. For example, plasma panel and LED (Light-Emitting Diodes).
- Non-Emissive Displays − Non-emissive displays use optical effects to convert sunlight or light from some other source into graphics patterns. For example, LCD (Liquid-Crystal Device).
- Printer:
Printer is an output device, which is used to print information on paper.
There are two types of printers −
- Impact Printers
- Non-Impact Printers
Impact Printers
Impact printers print the characters by striking them on the ribbon, which is then pressed on the paper.
Characteristics of Impact Printers are the following −
- Very low consumable costs
- Very noisy
- Useful for bulk printing due to low cost
- There is physical contact with the paper to produce an image
These printers are of two types −
- Character printers
- Line printers
Character Printers
Character printers are the printers which print one character at a time.
These are further divided into two types:
- Dot Matrix Printer(DMP)
- Daisy Wheel
Dot Matrix Printer
In the market, one of the most popular printers is Dot Matrix Printer. These printers are popular because of their ease of printing and economical price. Each character printed is in the form of pattern of dots and head consists of a Matrix of Pins of size (5*7, 7*9, 9*7 or 9*9) which come out to form a character which is why it is called Dot Matrix Printer.

Advantages
- Inexpensive
- Widely Used
- Other language characters can be printed
Disadvantages
- Slow Speed
- Poor Quality
Daisy Wheel
Head is lying on a wheel and pins corresponding to characters are like petals of Daisy (flower) which is why it is called Daisy Wheel Printer. These printers are generally used for word-processing in offices that require a few letters to be sent here and there with very nice quality.

Advantages
- More reliable than DMP
- Better quality
- Fonts of character can be easily changed
Disadvantages
- Slower than DMP
- Noisy
- More expensive than DMP
Line Printers
Line printers are the printers which print one line at a time.

These are of two types −
- Drum Printer
- Chain Printer
Drum Printer
This printer is like a drum in shape hence it is called drum printer. The surface of the drum is divided into a number of tracks. Total tracks are equal to the size of the paper, i.e. for a paper width of 132 characters, drum will have 132 tracks. A character set is embossed on the track. Different character sets available in the market are 48 character set, 64 and 96 characters set. One rotation of drum prints one line. Drum printers are fast in speed and can print 300 to 2000 lines per minute.
Advantages
- Very high speed
Disadvantages
- Very expensive
- Characters fonts cannot be changed
Chain Printer
In this printer, a chain of character sets is used, hence it is called Chain Printer. A standard character set may have 48, 64, or 96 characters.
Advantages
- Character fonts can easily be changed.
- Different languages can be used with the same printer.
Disadvantages
- Noisy
Non-impact Printers
Non-impact printers print the characters without using the ribbon. These printers print a complete page at a time, thus they are also called as Page Printers.
These printers are of two types −
- Laser Printers
- Inkjet Printers
Characteristics of Non-impact Printers
- Faster than impact printers
- They are not noisy
- High quality
- Supports many fonts and different character size
Laser Printers
These are non-impact page printers. They use laser lights to produce the dots needed to form the characters to be printed on a page.

Advantages
- Very high speed
- Very high quality output
- Good graphics quality
- Supports many fonts and different character size
Disadvantages
- Expensive
- Cannot be used to produce multiple copies of a document in a single printing
Inkjet Printers
Inkjet printers are non-impact character printers based on a relatively new technology. They print characters by spraying small drops of ink onto paper. Inkjet printers produce high quality output with presentable features.

They make less noise because no hammering is done and these have many styles of printing modes available. Color printing is also possible. Some models of Inkjet printers can produce multiple copies of printing also.
Advantages
- High quality printing
- More reliable
Disadvantages
- Expensive as the cost per page is high
- Slow as compared to laser printer
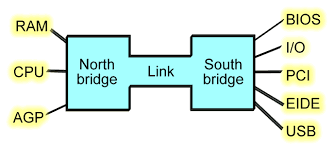
- North/ South bridge
The northbridge links the CPU to very high-speed devices, especially RAM and graphics controllers, and the southbridge connects to lower-speed peripheral buses (such as PCI or ISA). In many modern chipsets, the southbridge contains some on-chip integrated peripherals, such as Ethernet, USB, and audio devices.
Developing this technology explain all development things:
New types of storage devices such as versions of flash memory cards, hard disks using discs and technology of capability are the outcomes of progress in technology in hardware that is calculate. Computer motherboards have undergone changes. Despite the progress in functionalities and performance, these components’ purchase price has fallen. It is that place is taken by a struggle of developing technologies in computer hardware. The pace of growth of microprocessor increases as the competition between the chip manufacturing companies, AMD and Intel, intensifies. The companies are participating in a neck and neck competition and always outdo each other. In the area of computer peripherals, the most recent technology in computer hardware is in developing another edition of keyboard and mouse. The idea of keyboard and mouse is about a decade old. However, the growth of these items is a work in progress. Mouse and keyboard’s products are believed to be free and durable.
A few of the improvements in the technology in computer hardware are currently gearing up for altering the idea of notebook and desktop computers.
A new breed of computers will be introduced in future, with new improvements making possible the convergence of computers and cell phone technology. With no need for a mouse and with touch screen monitors, these gadgets are most likely to become the next huge leap in the continuously leaping development area.
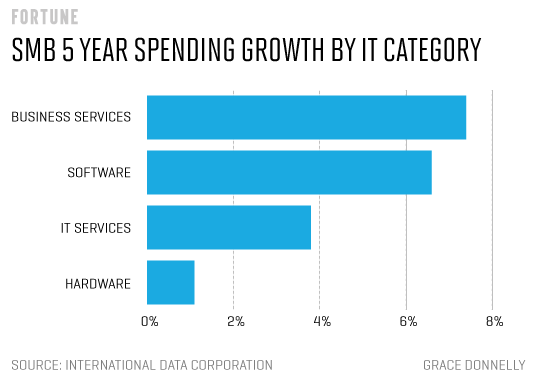
Growth level of hardware technology and its salary:
Spending by small and medium businesses (SMBs) on laptops, PCs, peripherals, and other hardware will show a just a 1.1% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) over the next four years compared to 6.6% growth in software spending, and 3.8% growth in IT services spending, according to IDC.
The most highly compensated computer hardware engineers work in research and development.
- Median Annual Salary: $114,600 ($55.10/hour)
- Top 10% Annual Salary: More than $172,630 ($82.99/hour)
- Bottom 10% Annual Salary: Less than $66,700 ($32.07/hour)
2021 current result:
From exascale computing to 5nm graphics cards and 8K gaming, the most anticipated products of the year 2021 will bring unprecedented innovation, speed, and performance.These are the most promising announcements and our predictions for next year’s computer technology evolution.
A year ago, no-one would have been able to foresee how 2020 would leave an indelible mark on our collective memory. The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on all areas of our lives, from how we work to how we communicate with each other. Throughout this experience, technology has played a big part in helping us cope and adapt to the new challenges. We’re now approaching the end of the year, and alongside the hopes for a vaccine that can finally ease restrictions to movement, we’re looking at what 2021 will bring for the computing tech sector. Several exciting announcements have been made for products that promise to revolutionize the computer industry. Below are some of our predictions based on the technologies we look the most forward to. With the new and upcoming range of GPUs (which, at present, already double the performance of their predecessors), 4K gaming could become more affordable in the PC world. Even 8K is a possibility with the next line of cards, like Radeon’s RDNA 2 architecture, which includes hardware-accelerated ray tracing and variable-rate shading. It’s been reported that several companies are also working on DDR5 RAM for PCs (LPDDR5 can already be found in the Samsung Galaxy S20 smartphone), a hint that the technology is waiting for more compatible CPUs to officially launch at a massive scale. Overall, 2021 looks like a very promising year for computer tech. With brand new hardware and more intelligent software, we will definitely see an industry boom in the months to come.
Future scope:
- Hardware and Networking is the most demanding career area among the young ones.
- Hardware is the most paying & fastest growing domain in the IT sector.
- Computer Hardware is the amalgamation of physical components or parts that creates the computer system. Physical components like monitor, keyboard, mouse, hard disk drive, graphic card, RAM, motherboard, etc.
- Hardware professionals deal with different hardware components such as chips, computer systems, motherboard, processor, RAM, circuit boards, modems, external hard disks, printers, and keyboards.
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
.png)
Comments
Post a Comment